Summary
Delighting a customer can be an uphill task if you don’t constantly innovate. You may ‘satisfy’ customers, but not ‘delight’ them. Innovation at every step of the customer journey – technology, product, process, service, etc. ensures a ‘wow’ factor each time a customer interacts with your brand. Employees form another important touchpoint and so working on employee engagement and motivation can significantly improve customer experience.
This article talks about innovating at various levels, the challenges encountered and how you can gain customer loyalty.
Table of Contents
- Summary
- Introduction
- Technological Innovation
- Product Innovation
- Process Innovation
- Service Innovation
- Innovation Challenges
- Importance of employee engagement
- Design thinking
- Conclusion
Introduction
Delivering the right experience remains the key component of success for companies differentiating their brand and offerings from one another. With an ever-evolving growth and demand pace, Innovation remains the driving force behind a company’s success. Enabling creative ways of engaging customers to deliver unique and memorable experiences requires a shift away from a product focus to a customer-centric focus. How can companies then remain relevant? We look at innovation from two paradigms – the outer view of the organization (listening to customer needs) and the inner view (listening to employees). We can then segregate innovations based on process, product, service and technology. In this article, we will explore the benefits, impacts and barriers faced within each facet of driving innovation. Ultimately the customer journey plays a vital role in understanding what, where and how innovation applies, but for the sake of keeping the reader engaged I won’t go into the customer journey mapping process itself or the importance of customer journey mapping and the tools associated with it.
Technological Innovation
Technology has undoubtedly revolutionized the way companies operate and interact with their customers. On the outer view, there is a widespread use of digital tools with the internet, smartphones and social media, allowing customers to be ever-connected to brands and also driving purchase and interaction decisions. The upside allows companies to personalize experiences with their customers, track customer lifetime values, and understand customer patterns and behaviors, all while keeping them informed.
Let’s take, for example, chatbots and AI-powered virtual assistants that provide support, accessibility and availability to customers at all times. With the inner view, companies can collect, automate and integrate how data flows between platforms providing powerful dashboards with insights that help foster quick decision-making alongside realizing ROI on key initiatives.
Machine learning algorithms and robotic process automation (RPA) allow companies to automate repetitive tasks, which in turn free up resource allocations helping save costs. Another use of emerging technologies lies in the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create exciting and immersive experiences. For example, real-estate companies now provide tools to allow customers a walk-through of properties, or even map out how furniture and artwork can be placed around. Similarly, retail companies provide platforms allowing customers to try out clothes, or shades of cosmetics, virtually to enhance the ease of purchasing online.
Of course, there are downsides to the use of technology, as not everyone can easily maneuver through these platforms. How often have you been frustrated trying to reach your bank with regards to a service only to be greeted by a virtual voice assistant that’s trained only to understand a small subset of the language used across multiple segments and personas of customers by eventually disconnecting your call and not letting you talk to an agent? Well, ChatGPT is a great example of algorithms learned well and with time we can only hope for these services to get trained and be better than the human connect. Or so I think anyway!
Product Innovation
Product Innovation, on the other hand, can be viewed through new product development or enhancement of existing products. By understanding customer needs and preferences, companies can deliver value to their customers in more meaningful ways. Different types of innovation can be used to improve product ease of use and increase accessibility or make the product more intuitive. Design changes to improve user experience, aesthetic appeal, or even grow product attractiveness within specific segments of buyers.
The ultimate goal of product innovation from a customer experience standpoint is to make the product more functional, reachable, usable, and also more enjoyable so as to meet the ever-evolving needs of the customers.
The real impact can be realized by driving long-term customer loyalty when the product is done right, and that’s the reason why companies should focus on listening to customers. Care should be taken when innovation in the new product development space is implemented because this could either enhance cross-sell opportunities or can also come at a price of impacting brand value. For example, a famous luxury brand lost its valuable clientele because it decided to diversify and make the same products (aka handbags) more accessible to a wider range of audience which in turn hurt its image and shareholder value as it lost customers who wanted to associate themselves with exclusivity.
So, while the outer view might dictate a need for a segment of affordability, from an inner view, they should strategize better to rebrand and disassociate. Elongating my point here, there are several high-value luxury brands that only provide a diversified range of products like cosmetics and perfumes that cater to a larger segment of buyers. This strategy allows for the brand association but not the primary products.
Process Innovation
A derivation of total quality management (TQM), the ultimate goal for process innovation remains improving efficiency and productivity while reducing friction in the company, which in turn requires rethinking and redesigning the way work is done within companies. From an outer view, this involves increasing convenience for customer interactions with company services. Simple examples include streamlined logistics services that enable customers to understand exactly when their products will be delivered, including abilities to track the logistics delivery stages or reach the right customer contact agent to clarify doubts, concerns, or issues. Companies then need to have mechanisms to track issues and close the loop.
From the inner view, companies can utilize technology to automate their processes, track process efficiencies and derive information on the productivity of resources. The outerloop is a mechanism that allows for operational efficiencies to be tracked by companies and associate the inner and outer views more efficiently. Order delivery and fulfillment systems are the best examples of improving customer journey by using intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
Communication remains key, but providing the right messaging that delivers empathy for process-gone-wrong is an important aspect of consideration as well. Further use of data analytics and insights can inform decisions around broken processes that might be unknown to the company. QuestionPro’s NPS+ allows for collecting feedback alongside ideas for improving customer experiences which, at a deeper level, allows companies to realize customer churn. Data can also help analyze customer behaviors and preferences that can help improve the process delivery.
Service Innovation
The most important component of service delivery is creating new and unique ways in which service value is delivered to customers. Personalization in service delivery makes experiences memorable! Equally important is the inclusion of empathy when communicating with customers. In the digital world we live in, digitizing empathy is very important to include the right communication when dealing with issues faced by customers. Service innovation means delivering personalized experiences, for example, offering bespoke packages that are tailored to their preferences and needs, and providing offers and recommendations alongside access to exclusive events and experiences. Service channels can also be expanded to include multiple touchpoints, offering 24/7 support with physical and digital touchpoints spanning across social media and other channels.
Innovation Challenges
While innovation in the customer experience space can have multiple benefits, it comes with potential issues and challenges that need to be addressed. It’s worth noting these down before we tackle how best to address these problems:
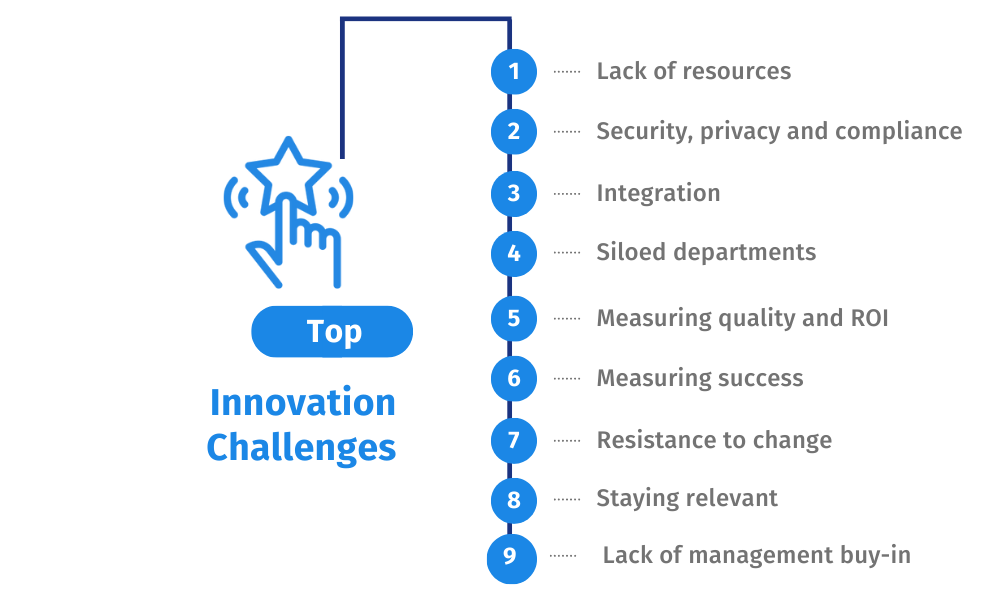
- Lack of resources or costly: It goes without saying it’s expensive to innovate, ideate and incorporate changes within an organization. With the bottom line of adding value to customers, the top line should not suffer the costs that cannot be realized. Dedicated teams, resources and technology come at a cost that can be rewarding if done right.
- Security, privacy and compliance: Most important to consider in this digital age when using technologies and data analytics is handling how data is captured and stored. Consensus is an important topic in many countries and transparency is key in the use of customer data. Hence security and privacy policies need to stay in compliance with protecting customer data that needs to be customized geographically as well. IT and security systems need to be then robust as any small glitches can hurt the brand, as we’ve seen far too often.
- Integration: Considerable efforts are required to understand the business architecture and integrate it with existing systems remains important for seamless data transition between multiple databases, including CRM, ERP and other business sources. This allows for a unified view of the data but will involve bringing together multiple teams to understand what and why data resides where it does.
- Siloed departments: Large organizations face difficulties in coordinating efforts for innovation across multiple departments that especially work in silos. Lack of unification and sharing data and information create hindrances to innovating in the right direction and avoiding redundancies.
- Measuring quality and ROI: If innovation efforts do not have a way to realize their value, how quality is enhanced and maintained and the overall value it creates, then the efforts of innovating are in vain. Continuous testing and validating these efforts to ensure they are not causing additional hindrances to both the inner and outer view are important.
- Success measurements: Effective means to measure customer experience in the process of innovation are important and companies tend to fail within these aspects. Continuous data collection, analysis and inferences come at additional time and cost to resources.
- Resistance to change: The biggest parameter to why companies fail to innovate is the resistance to change from employees and the culture to incorporate risk. Usually, a lack of understanding of the real benefits of innovating causes resistance to acting upon these initiatives. Lack of effective communication and building a culture that fosters innovation are key reasons for these failures.
- Staying relevant: Keeping up with the pace of industry change and uncertainty that is rapidly evolving, understanding customers changing demands and expectations timely, and adopting research, strategy and technology are downfalls to innovating.
- Lack of management buy-in: Incorporating all the downfalls from the points listed so as to help create a solid business case takes dedicated teams and efforts in getting management buy-ins. This lack of coordination will create issues not just while implementing changes but also while realizing them.
Importance of employee engagement
Innovation begins from the inner view, with employees playing the most critical roles in understanding and helping translate customer needs to organizations that can, in turn, empower innovation. How can organizations then empower employees to help elevate the innovation process?
- Innovation Culture: Fostering a culture of innovation should be the starting point towards encouraging employees to put forth their recommendations, provide ideas, enhance creativity, encourage experimentation and provide clear vision and mission statements to establish support.
- Recognition: Organizations should not only recognize but reward employee contributions towards the innovation space. This helps encourage bringing new ideas or enhancements to the table, helps enable risk-taking and, with the right support, helps carve out a path to implement valuable proposals. For example, many large organizations focus on patenting and trademarking ideas that are proposed by employees and offer platforms that identify and push ideas through multiple stages. The support extends to providing time and possibly an alternative career roadmap so that employees are encouraged to pursue their ideas without the pressure of doing everything else.
- Encourage ideation: Clear communication encouraging employees to ideate should be made a part of the primary agenda so that improvements to process, product and service can be put forward. Hackathons, brainstorming sessions and providing suggestions and feedback mechanisms are some ways to encourage ideation.
- Training and development: Organizations should invest time in training their employees to understand the importance of innovation and provide programs to include the process for innovation. New skills and knowledge sharing can be extremely helpful in elevating how employees think about problem-solving and innovation.
- Cross-collaboration: Large organizations can face issues with working in silos, and it’s important to bring access to multiple functionalities that exist across different teams so that employees are encouraged to collaborate across the board with the right subject matter expertise and possibly across tiers. These efforts would increase the value of the ideas brought forward as they get better perspectives when they work across teams.
- Encourage and provide constructive feedback: There needs to be considerable encouragement in educating the benefits of innovating. Not all ideas will be feasible, but feedback should be provided constructively so as to continue encouraging innovation.
- Resources and experimentation: The ideation process can go through multiple stages, including research and experimentation, to assess the viability of implementation. Organizations should consider providing the right tools for innovation, resources and guidance, which include allocating budgets toward innovation.
- Implement agile methodologies: A continuation of experimentation involves rapid prototyping, A/B testing and creating proof of concepts (POC) to get quick management buy-ins.
- Crowdsource ideas using technology: Platforms like IdeaScale enable organizations to gather both the inner and outer views for enhancing their abilities through the generation of ideas not just from employees but also through customers.
- Measure success: Many a time, I have found this element to contradict the intentions to grow innovation, but that is only because organizations have not thought through all the different ways to evaluate ideas. In the CX space, it’s easier to go back and check how customers feel about new additions by gauging their feedback and accessing the impact of the idea. However, KPI’s need to be put in place and re-evaluated where required to cater to the diversified ideas that can be brought to the table.
Design thinking
Last but definitely not least, design thinking should be considered an important tool to access innovation in the customer experience space. The principles that govern design thinking should be defined so that the organization uses a ‘Customer-first’ model allowing organizations to remain Customer-centric. By maintaining the target audience in mind, even internal processes can be enhanced so as to enhance the outer view of the customers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, innovation requires planning, needs a clear strategy, ownership and also the right communication so as to encourage stakeholders to ideate, keeping the right objectives in mind. There are bound to be challenges along the way, but if designed well, organizations will benefit by gaining memorable experiences and hence customer loyalty.

