
Stratified sampling is a sampling procedure in which the target population is separated into unique, homogeneous segments (strata), and then a simple random sample is selected from each segment (stratum). The selected samples from the various strata are combined into a single sample. This sampling procedure is sometimes referred to as “occasional fee sampling.”
In this article, we’ll explore the foundations, types, and applications of stratified sampling and compare it to other sampling methods, including quota sampling, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each approach. Read below about some of the considerations to remember for the best capture.
What is Stratified Sampling?
Stratified sampling is a way to obtain a representative sample from a community that researchers have split into similar groups (called “strata”). Researchers use this technique to ensure that their sample includes members of certain classes and to make accurate estimates of each group’s characteristics.
This type of probability sampling, called “stratified random sampling,” is used in numerous research projects to learn more about the differences between subpopulations.
In the first step of the stratified sampling method, researchers divide a diverse community into mostly the same groups. These groups are called strata, which is the plural of the stratum.
Then, they take random samples from each group (called a “stratum”) and combine them to make a full sample representative of the whole. Learn more about representative groups. Quota sampling is when researchers choose subjects from the groups nonrandomly.
Strata are smaller groups of people who are mostly the same as each other compared to the whole community. Researchers can divide groups into classes based on income, gender, race, etc.
For example, if your research question asks you to compare how things turn out for people with different incomes, you might divide the groups by income. There should only be one stratum for the whole community.
Selection Steps for a Stratified Sampling Survey
Stratified sampling is a technique used to ensure that various subgroups (or strata) within a population are adequately represented in the sample. There are eight main steps in selecting a stratified random sample:
Step 1: Define the target population
Clearly define the population you want to study, specifying the characteristics and boundaries of the population.
Step 2: Identify stratification variables
Determine the key characteristics or variables for dividing the population into meaningful subgroups or strata. These variables should be relevant to the research objectives and help create distinct groups within the population.
Step 3: Determine the number of strata
Based on the identified stratification variables, decide how many strata to create. The number of strata should be determined by the variability within the population and the level of precision required for the study.
Step 4: Develop or identify a sampling frame
Obtain or create a sampling frame that includes information on the stratification variables for each item in the target population. A sampling frame is a list or database representing the population from which the sample will be selected.
Step 5: Evaluate the sampling frame
Assess the sampling frame for issues such as undercover (missing elements from the population), overcover (duplicated or irrelevant elements), multiple listings, or clustering. Adjust the frame as necessary to ensure its accuracy and appropriateness for sampling.
Step 6: Divide the sampling frame into strata
Divide the sampling frame into separate strata based on the identified stratification variables. Each element in the population should be assigned to one and only one stratum, ensuring that the strata are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive.
Step 7: Determine the sample size for each stratum
Decide on the desired sample size for the overall survey and the sample size for each stratum. The sample size for each stratum should be determined based on the proportion of the population that belongs to that stratum. This ensures that each stratum is represented appropriately in the final sample.
Step 8: Randomly select samples from each stratum
Randomly select the specified number of items from each stratum using random sampling techniques. This ensures that each element in the population has an equal chance of being selected and allows for representative sampling within each stratum.\
If you want to learn more about “Stratified Random Sampling” then read this blog: Stratified Random Sampling: Definition, Method and Examples
Subtypes of Stratified Sampling
There are two main subtypes of stratified sampling: Proportionate and disproportionate sampling.
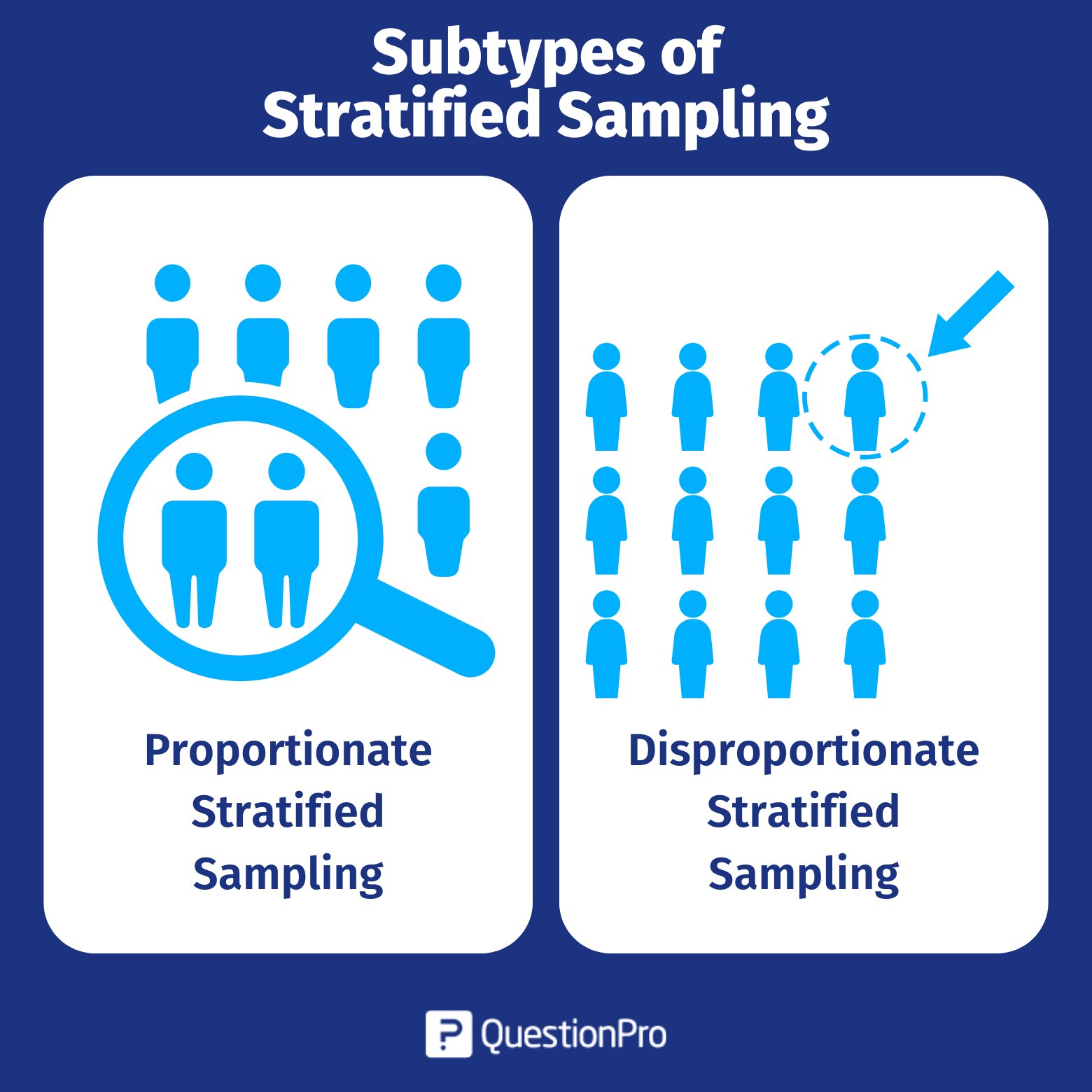
Proportionate Stratified Sampling
In proportionate stratification, the number of items assigned to various strata is proportionate to the strata’s representation of the target population. That is, the final sample size drawn from each stratum is proportionate to the relative size of that stratum of the target population.
The sampling fraction is applied to each stratum, giving each population element an equal opportunity to be selected. The resulting sample is self-weighted. This sampling technique is used when the research aims to estimate population parameters.
The researcher often wishes to estimate population parameters, conduct detailed analyses within a relatively small stratum, and compare strata with each other. Proportionate stratified random sampling may not result in some of the strata of this type of analysis.
Taking the example described in our table, it would not be possible to carry out a detailed analysis of the elements in zone 2 since only 12 of the elements are found in the sample.
Furthermore, the comparison of the elements of Zone 2 with the other zones would be doubtful.
Disproportionate stratified sampling may be a better choice for carrying out this type of analysis.
Disproportionate Stratified Sampling
Disproportionate sampling is a procedure in which the number of elements included in the sample from each stratum is not proportionate to their representation in the total population. The elements of the population do not have an equal chance of being included in the sample. The same sampling fraction does not apply to each stratum.
On the other hand, the strata have different sampling fractions, so this sampling procedure is not an equiprobable selection. The population composition must compensate for the sample’s disproportion to estimate the population parameters. However, for some research projects, disproportionate stratified sampling may be more appropriate than proportionate.
Disproportionate sampling can be divided into three subtypes based on the purposes of our assignment.
For example, it could facilitate strata analysis, focusing on optimizing cost, accuracy, or both accuracy and costs.
A study’s objective may require a researcher to carry out a detailed analysis of the sample strata. If proportionate stratification is used, the sample size of a stratum is very small; therefore, it may be challenging to meet the study’s goals.
The proportionate allocation may need to produce more cases for this type of detailed analysis. One option is to oversample small or infrequent strata. Such oversampling would create a disproportionate distribution of sample strata compared to the population. However, there may be sufficient cases to carry out the strata analysis required for the study.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Strengths and Weaknesses of Stratified Sampling
Stratified sampling has many strengths and weaknesses associated with most probability sampling procedures compared to non-probability sampling procedures.
Compared to simple random sampling, the strengths of stratified sampling include the following:
Strengths of Stratified Sampling:
- Enhanced Representation: Stratified sampling ensures that all subgroups within a population are represented, leading to more accurate and reliable results. This is particularly beneficial when certain strata are small but important to the study.
- Increased Precision: By reducing variability within strata, stratified sampling often yields more precise estimates than simple random sampling, especially when significant differences exist between strata.
- Tailored Analysis: Researchers can analyze data for specific strata, allowing for a deeper understanding of population variations and identifying trends or patterns.
- Resource Efficiency: Stratified sampling can be more efficient in terms of time and costs, mainly when targeting specific subgroups rather than sampling randomly across a larger population.
Weaknesses of Stratified Sampling:
- Complexity in Implementation: Designing a stratified sample requires a clear understanding of the population and accurate identification of strata, which can be complicated and time-consuming.
- Potential for Misclassification: Incorrectly defining or classifying strata can lead to biases and affect the validity of results.
- Limited Applicability: Stratified sampling may not be appropriate for populations with no clear strata or homogeneous populations, where simple random sampling might suffice.
- Resource Intensity: Ensuring accurate stratification and random selection within each stratum may require more time and effort.
What is the Difference Between Stratified Sampling, Sampling, and Quota Sampling?
Stratified sampling and quota sampling are similar to each other. Both involve dividing the target population into categories and then selecting a certain number of items from each category. Both procedures have as their main objective the selection of a representative sample and/or the facilitation of subgroup analysis. However, there are important differences.
Stratified sampling, sampling, and quota sampling are all techniques used in research to select participants or observations from a population. However, they differ in methodology, objectives, and implementation. Here’s a breakdown of each:
1. Sampling
- Definition: Sampling is a general term for the process of selecting a subset of individuals from a larger population to estimate characteristics or gather information about that population.
- Purpose: The primary goal is to make inferences about the entire population based on observations from the sample.
- Types: Sampling can include various methods, such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
2. Stratified Sampling
- Definition: Stratified sampling is a specific type in which the population is divided into distinct subgroups (strata) based on certain characteristics (e.g., age, gender, income). A random sample is then drawn from each stratum.
- Purpose: This method ensures that all subgroups are adequately represented in the sample, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
- Advantages: It reduces variability within strata and allows for detailed analysis of specific subgroups, enhancing the overall precision of the estimates.
3. Quota Sampling
- Definition: Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where researchers ensure that specific characteristics or traits are represented by setting quotas for different subgroups. Participants are selected until these quotas are met, regardless of their selection probability.
- Purpose: The objective is to ensure that certain population characteristics are reflected in the sample, often for convenience or cost-effectiveness.
- Limitations: Because it does not involve random selection, quota sampling may introduce bias and limit the generalizability of results. The sample may not be truly representative of the population.
Summary of Key Differences
| Feature | Sampling | Stratified Sampling | Quota Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Divide the population into strata and samples randomly from each | To ensure the representation of subgroups for accurate results | Ensures representation of specific characteristics by setting quotas |
| Purpose | To estimate population characteristics | To achieve the representation of certain traits efficiently | Varies by the method used |
| Selection Method | Can use various methods | Random selection from each stratum | Non-random selection until quotas are met |
| Bias Risk | Varies by method used | Lower bias if strata are defined well | Higher risk of bias due to non-random selection |
| Generalizability | Depends on the sampling method | Generally higher due to random selection | Limited due to potential bias |
Understanding these differences helps researchers choose the appropriate sampling method based on their study’s goals, resources, and population characteristics.
Finally, we share an article on the characteristics of another type of sampling, systematic sampling, cluster sampling.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between sampling methods is crucial for selecting the best approach for any research study. Stratified sampling, emphasizing subgroup representation, offers precision, especially when population diversity is a key factor. By contrast, quota sampling provides a more flexible, non-random method often suited for time-sensitive or budget-conscious studies.
While each method has unique advantages and challenges, knowing when and how to use them can significantly enhance the validity of research findings. Equipped with this knowledge, researchers can design surveys and studies that yield actionable insights, ensuring they draw the most accurate conclusions about their target populations.
Solve your research challenges with simple-to-create surveys that provide complex, real-time insights. Leverage custom point-and-click logic, advanced question types, and integrations and create mature, complex research models for choice-based, consumer, and more research.







