Customer data management is more important than ever in today’s world of information. And the rewards of this big data revolution might be enormous for both businesses and customers. It’s enabling companies to improve their customer journey, personalizing client experiences by making better data-driven decisions.
However, maintaining and preserving all of this data comes with its own set of difficulties. Only by following best practices you will be able to overcome these obstacles. And it provides a genuinely exceptional customer experience.
Let’s take a look at what customer data management is before we get into any specific recommendations.
What is customer data management?
Customer data management is the practice of gathering, organizing, securing, and storing data in an organization. As a result, it can be used to make business decisions. Businesses are generating and consuming data at alarming rates. Customer data management solutions are becoming increasingly important.
The most advanced customer data management software on the market today ensures that decisions are always based on reliable, up-to-date data. The software assists with everything from data preparation to cataloging, search, and management, allowing users to find the information they need for analysis quickly.
Data Asset Management involves the strategic and organized handling of customer data to ensure its accuracy, security, and accessibility throughout its lifecycle. This process includes collecting, storing, processing, and analyzing customer information while adhering to privacy regulations. It is a important part of data management.
Data collection, under the framework of data governance, can be gathered and kept in a database from a variety of sources. Teams then analyze the information to better understand clients and their demands.
LEARN ABOUT: Client Management
Why customer data management is important?
Customer data management is essential in implementing effective data analysis at scale. It produces crucial insight that adds value to your customers while improving your bottom line. People across an organization can find and access trusted data for their queries with effective data management. Here are some reasons why customer data management is essential:
Improve decision making
Accurate data is the most powerful asset of a company. Customer data management improves decision-making around product improvement, marketing campaigns, and customer relationships.
Reduced data loss
It reduces the risks of data loss or any kind of loss. Relying on safe and reliable sources helps reduce data loss.
Better customer data security
Conscious customer data management procedures assist in keeping such personal data, such as contact information, addresses, bank account details, etc., secure in social media, where all of our sensitive and personal data is easily accessible.
Lower costs
Suppose organizations follow customer data management strategies from the start. In that case, there will be less chance to spend on solving poor management issues, and they can save a fortune and successfully run the business smoothly.
Increased efficiency and productivity
Suppose all the above practices are followed diligently, and the available data is accurate and reliable. In that case, this will eventually result in increased efficiency and productivity of the employees in the organization. Since they can perform their tasks in less time, giving them more productivity.
Now that we know what customer data management is, let’s review some practices and steps to do it.
Customer data management process
The procedure of customer master data management is fairly similar to the whole MDM process.
It entails collecting data from many sources and systems, including customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and assigning customer identifiers to data so that customer groups records. We’ll look at four steps of customer data management to provide a better customer experience.
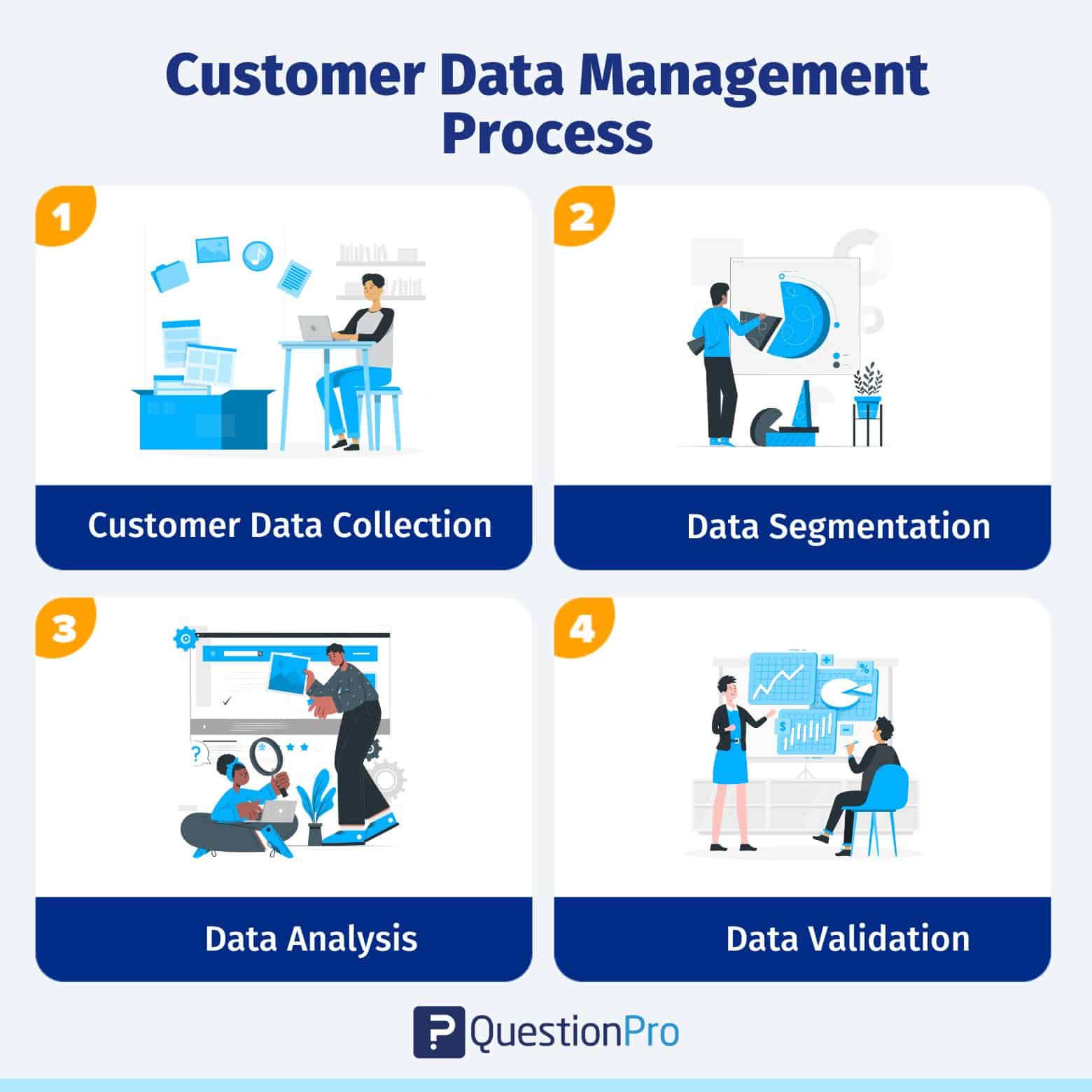
Customer data collection
The first step is to establish procedures for collecting customer data. To collect data, you’ll need a single client database management system. Information can be collected through various channels. It is based on the various methods that your organization has put in place.
For example, it could be collected data from forms submitted by customers or behavioral data tracked with monitoring tools.
Data segmentation
Data segmentation is an important aspect of customer data management because it helps create distinct and identifiable data clusters, which are important in the final step of this exercise. Using tools and segmentation techniques, you can create detailed customer profiles and data stacks.
Because each function uses data for a different purpose, the customer information requirements for sales, marketing, and customer service differ. It is difficult to determine who has access to this data and what they can do with it without behavioral segmentation.
Data analysis
You can begin exploring the data for valuable insights once the data has been separated. And detailed customer profiles have been defined. The goal of data analysis is to develop specific initiatives that address individual customer needs. You can generate team-specific reports using analytics and other software at your disposal to aid decisions made by various departments.
Data validation
Once all the information is in place, the final step is to move it into the appropriate customer data management systems. Different departments will access your customer data infrastructure via various customer data platforms to enable data-driven decision-making.
This necessitates the use of protocols to connect all of their tools to the central data engagement platform. In place to efficiently manage customer data. This customer data integration enables marketers, salespeople, and other groups to use real-time data for various purposes. Automated data validation tools can help with this process.
QuestionPro recently published a blog about Knowledge Management Software. You can check it out for a better understanding.
6 Best practices for customer data management
A lot goes into proper customer data management. Here are some essential practices you can follow to manage customer data effectively:
Practice 1: Organizational ownership
To begin, you must decide which internal team will “own” customer data. This group or individual will be in charge of all subsequent considerations. While they will undoubtedly cooperate with others along the way, they are ultimately responsible for the data. So, who exactly should be in charge of customer data?
We get this question a lot, and the answers are evolving. Traditionally, customer data is owned by a team such as Marketing, Sales, or Customer Success. However, we have recently seen some new roles arise to take the lead in managing customer data within the organization.
Practice 2: Types of data
Next, you must decide what types of customer data your company will collect. Typically, this should include both identities and attribute data (who they are) in addition to behavioral data (what actions they took).
This step requires you to consider not only what data you want to collect but also the sources of data from which that data will be derived. As you do so, take inventory of the various sources containing the data you seek, keeping in mind that some of the data may be stored in locations you do not visit daily.
Practice 3: Data storage
Once you’ve decided what kinds of data you’ll collect, you must decide where that data will be stored. Will you, for example, keep it separate across different tools, or will you consolidate the data in one central location?
You can make both options work. However, centralizing data in a single location is the most effective way to keep teams on track. You can centralize customer data management using internal resources and data warehouses. Or you can use a customer data platform (CDP).
Practice 4: Security and privacy
When considering data storage, you must also consider (and respond to) how you wish to meet data privacy and security requirements. Financial services and healthcare, for example, face industry-specific considerations.
If you work in one of these highly regulated industries, you should be aware of the standards. You must meet and come up with a plan for doing so.
Practice 5: Data quality
Getting all of your customer data in one place is one thing in effective customer data management. Another challenge is keeping that data clean and up to date over time. This type of continuous data quality effort is frequently overlooked. However, it is important for long-term success.
This is because, in the absence of proper processes and controls, your data can quickly become unstable. So, how do you keep your data clean and current? Leading annual or quarterly data refreshes that include data enrichment activities is a good place to start. You can also use data standardization and validation to help with these efforts.
Practice 6: Activation
Last but not least, you must determine which tools in your tech stack will ultimately require data to power them. Customer relationship managers, marketing automation, and sales enablement solutions are common tools to which organizations typically push customer data for activation. The tools that require data will be determined by your goals and the strategies you implement to achieve those goals.
LEARN ABOUT: Consumer Decision Journey
How QuestionPro helps as a data management tool?
QuestionPro is a comprehensive customer data management platform offering various features and tools to effectively gather, organize, analyze, and derive insights from data. Here’s how QuestionPro helps as a customer data management tool:
- Data collection: QuestionPro provides a range of survey and data collection tools, including online surveys, forms, polls, and more. These tools allow you to collect data from various sources, such as customers, employees, or research participants.
- Survey design: The platform offers an intuitive interface to create customized surveys with different question types, logic, and design elements. This ensures that you collect the right data points from your target audience.
- Data storage and security: QuestionPro securely stores the collected data, ensuring data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR. It employs encryption and secure storage practices to protect sensitive information.
- Data integration: The platform allows you to integrate data from various sources, such as CRM systems, email lists, and more. This facilitates a holistic view of your data, enabling you to analyze and derive insights from diverse datasets.
- Data cleaning and preparation: QuestionPro provides tools to clean and preprocess collected data, ensuring accuracy and consistency. This step is crucial for meaningful analysis.
- Data analysis: The platform offers robust data analysis tools, including customizable reports, dashboards, and visualizations. This helps you make informed decisions based on the insights generated from the data.
- Collaboration: QuestionPro supports collaboration among team members working on data analysis and interpretation. You can share reports, insights, and data visualizations with relevant stakeholders.
- Data governance: To ensure data quality and compliance, QuestionPro incorporates data governance features. This includes permissions management, version control, and audit trails, allowing you to track changes and maintain data integrity.
- APIs and integrations: The platform provides APIs and integrations with other software applications, enabling seamless data flow between different tools you may be using.
Are you looking for ways to better understand your customers? Check out QuestionPro’s latest blog discussing their Customer Insight Platform!
Conclusion
Customer data management is important for any company that intends to use data to improve customer communication and connection.
Starting with the six considerations outlined here will help your team think about more than just how to manage and use customer data. And, once you’ve begun with consumer data management, you’ll be well-positioned to use the data your company has been collecting for years to drive meaningful business results.
With QuestionPro, you have access to consumer data management. This allows you to collect and analyze customer data and insights. You can use InsightsHub, the unified hub for customer data management, to organize, explore, search, and discover your research data in one organized data repository by leveraging the consolidated platform.
Frequently Asking Questions (FAQ)
Customer data management refers to the practice of collecting, organizing, and securely storing data about your customers to make informed business decisions.
Effective customer data management enhances customer understanding, personalization, and overall business strategies.